This is part of an exercise I want to do where i put myself in the shoes of software engineers and think about how they probably approached solving software engineering problems.
Scope
- A user can login into spotify on multiple devices
- If a user is playing a track on their browser this track and it's currently seeked position should be synced across multiple devices
Disclaimer!!! I'm not really sure of how spotify is able to achieve this. I didn't see any blog post on their engineering blog about this. The most information i have gotten is from inspecting their http requests during music streaming, which tells something but not much
Design dive-in
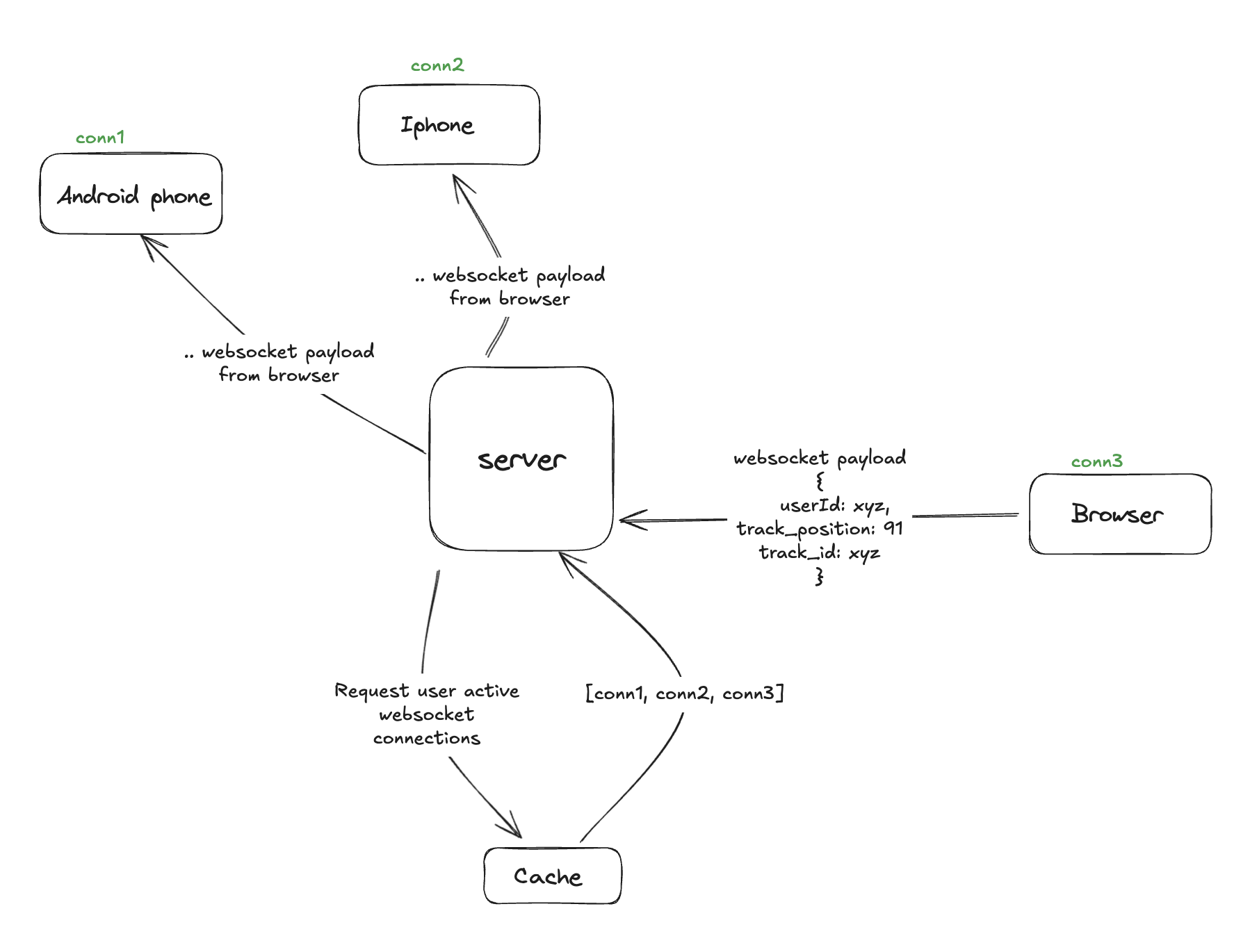
- The user logs in via a device, in this instance the browser(we'll give it the connection id conn3) starts streaming music
- The browser establishes a websocket connection with the api and starts sending the state of the currently playing music
-
Data would look something like
{ userId: xyz, track_position: 134, track_id: abcdef, }
-
- The websocket we just establised we'll store in memory, Something like redis would be useful for this but I don't see redis would store a network process that could actually be retrieved and used to send messages again. I could be wrong though but for now we'll save the cache in memory.
- Data would look something like:
{ userID: [conn3] } - The server would send pings to other devices to make sure they're still connected so as to know if to send data to them. If a client doesn't send a signal then we remove it from the the cache
- Data would look something like:
- The browser establishes a websocket connection with the api and starts sending the state of the currently playing music
- The user logs in from an android mobile device
- It establishes a websocket(conn2) to the server, again this connection is saved in memory like so:
{ userID: [conn3, conn2]} - The user logs in from another apple device
- It establishes a websocket(conn1) to the server, again this connection is saved in memory like so:
{ userID: [conn3, conn2, conn1]} - When the server gets music streaming data on the websocket between it and the browser(conn3) it checks the payload for the user id. Retrieves currently established connections and then broadcasts the streaming state data on those connections.
- The listening clients in turn update their currently playing state.
- If the same
track_idthey don't have to change the song but have to update the track position using thetrack_positionfield.
- If the same
What happens if a devices gets disconnected
The api sends regular heartbeats, "pings", to the connected devices. If it doesn't return a response we can safely assume it has been disconnected and remove it from the user's connection cache. We may also consider waiting for more than one ping before disconnecting(removing a device from cache) a device.
Design Overview